前言
本文所有算法题目来源均为 力扣(LeetCode)。
本篇主要记录链表相关算法题目,链表(Linked List)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的指针(Pointer)。由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到O(1)的复杂度,比另一种线性表顺序表快得多,但是查
找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要O(n)的时间,而顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是O(logn)和O(1)。
使用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
06 从尾到头打印链表
题目描述
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
解法1 栈实现
栈是属于先进后出的,可以通过先把链表入栈,然后出栈相当于链表反转,遍历输出每个节点的值。
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] arr = new int[size];
for (int i=0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.pop().val;
}
return arr;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
解法2 递归法
先走至链表末端,回溯时依次将节点值加入列表 ,这样就可以实现链表值的倒序输出。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
reverse(head);
int size = list.size();
int[] arr = new int[size];
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
arr[i] = list.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
private void reverse(ListNode node) {
if (node != null) {
reverse(node.next);
list.add(node.val);
}
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
单链表实现约瑟夫环问题
约瑟夫问题:已知n个人(以编号1,2,3…n分别表示)围坐在一张圆桌周围。从编号为k的人开始报数,数到m的那个人出列;他的下一个人又从1开始报数,数到m的那个人又出列;依此规律重复下去,直到圆桌周围的人全部出列。
实现约瑟夫环共3步:
- 1.首先将单链表构成环
- 2.根据约瑟夫环规则,删除节点
- 让循环继续,直到环中只剩下最后一个节点
代码实现
package com.cn.algorithm.linklist;
class ListNode {
int data;
ListNode next;
}
public class JosephCircle {
public static ListNode JosephCycle(ListNode first,int k){
//第一步:链表构成环
ListNode tail = first;
while (tail.next != null){
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = first;
//第二步删除
ListNode cur = first;
while(cur.next != cur){//当链表中的节点只剩下最后一个时,跳出循环
ListNode prev = null;
for(int i = 0;i<k-1;i++){
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
} // cur就是要删除的点
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = null;
cur = prev.next; // 让循环继续
}
cur.next = null;
return cur;
}
public static void print(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.println(head.data);
head = head.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n1 = new ListNode();
ListNode n2 = new ListNode();
ListNode n3 = new ListNode();
ListNode n4 = new ListNode();
n1.data = 1;
n2.data = 2;
n3.data = 3;
n4.data = 4;
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
JosephCycle(n1,3);
print(n1);
}
}
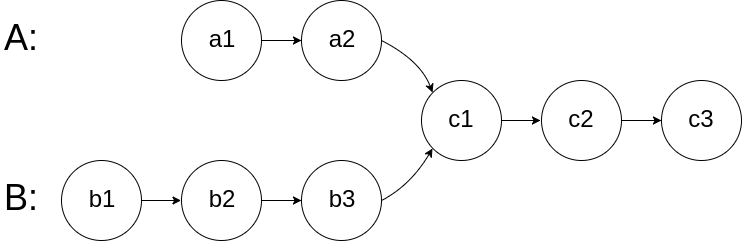
160 相交链表
题目描述
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
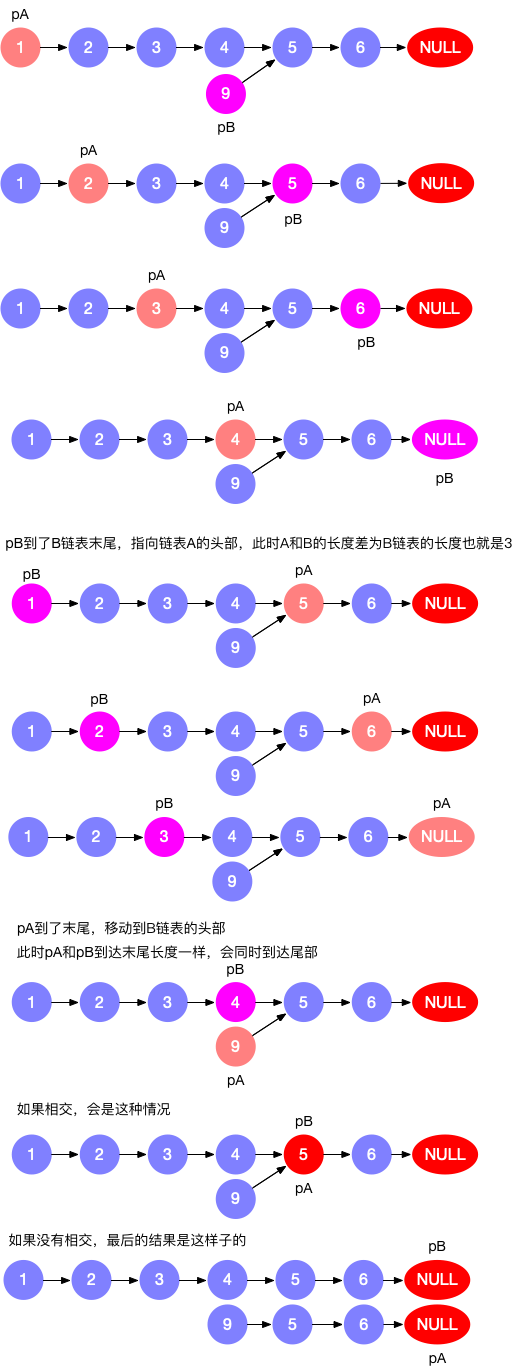
解法1 双指针法
消除长度差,交换上下指针。设定两个指针分别指向两个链表头部,一起向前走直到其中一个到达末端,另一个与末端距离则是两链表的 长度差。再通过长链表指针先走的方式消除长度差,最终两链表即可同时走到相交点。
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法2 Set实现
先遍历链表a,将a链表的所有节点放入一个set中。之后再遍历b链表,如果b链表的某个节点出现在set中,那么就找到了第一个相交的节点。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
Set set = new HashSet();
ListNode p = headA, q = headB;
while (p != null) {
set.add(p);
p = p.next;
}
while (q != null) {
if (set.contains(q)) {
return q;
}
q = q.next;
}
return null;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
206 反转链表(🌟)
题目描述
反转一个单链表。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
解法1 递归法
通过如下图片帮助理解。

代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
解法2 头插法
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
// 保存下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newHead.next;
newHead.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法3 双指针迭代(头插法)
申请两个指针,第一个指针叫 pre,最初是指向 null 的。第二个指针 cur 指向 head,然后不断遍历 cur。
每次迭代到 cur,都将 cur 的 next 指向 pre,然后 pre 和 cur 前进一位。都迭代完了(cur 变成 null 了),pre 就是最后一个节点了。

代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
21 合并两个有序链表
题目描述
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4 输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
解法1 递归法
如果 l1 或者 l2 为 null ,只需要返回非空链表。否则,我们要判断 l1 和 l2 哪一个的头元素更小,然后递归地决定下一个添加到结果里的值。如果两个链表都是空的,那么过程终止,所以递归过程最终一定会终止。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l2.next, l1);
return l2;
}
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n+m)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n+m)$ |
解法2 迭代法
设定一个哨兵节点
prehead,让我们比较容易地返回合并后的链表。我们维护一个 prev 指针,我们需要做的是调整它的 next 指针。然后,我们重复以下过程,直到 l1 或者 l2 指向了 null :如果 l1 当前位置的值小于 l2 ,我们就把 l1 的值接在 prev 节点的后面同时将 l1 指针往后移一个。否则,我们对 l2 做同样的操作。不管我们将哪一个元素接在了后面,我们都把 prev 向后移一个元素。在循环终止的时候, l1 和 l2 至多有一个是非空的。由于输入的两个链表都是有序的,所以不管哪个链表是非空的,它包含的所有元素都比前面已经合并链表中的所有元素都要大。这意味着我们只需要简单地将非空链表接在合并链表的后面,并返回合并链表。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(-1);
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
ListNode prev = node;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return node.next;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n+m)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
83 删除排序链表中的重复元素
题目描述
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
输入: 1->1->2->3->3 输出: 1->2->3
解法1 直接法
由于输入的列表已排序,因此我们可以通过将结点的值与它之后的结点进行比较来确定它是否为重复结点。如果它是重复的,我们更改当前结点的 next 指针,以便它跳过下一个结点并直接指向下一个结点之后的结点。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法2 递归法
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head.val == head.next.val ? head.next : head;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
19 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目描述
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2. 当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
解法1 两次遍历法
要删除链表的倒数第n个节点,问题可以转化为删除从列表开头数起的第 (L−n+1) 个结点,其中 L 是列表的长度。
首先添加一个辅助哑结点,该结点位于列表头部。哑结点用来简化某些极端情况,例如列表中只含有一个结点,或需要删除列表的头部。在第一次遍历中,我们找出列表的长度 L。然后设置一个指向哑结点的指针,并移动它遍历列表,直至它到达第 (L−n) 个结点那里。我们把第 (L−n) 个结点的 next 指针重新链接至第 (L−n+2) 个结点,完成算法。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dump = new ListNode(0);
dump.next = head;
int length = 0;
while (head != null) {
length++;
head = head.next;
}
length = length - n;
head = dump;
while (length > 0) {
length--;
head = head.next;
}
head.next = head.next.next;
return dump.next;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法2 双指针法
使用两个指针进行遍历。第一个指针从列表的开头向前移动 n+1 步,而第二个指针将从列表的开头出发。现在,这两个指针被 n 个结点分开。我们通过同时移动两个指针向前来保持这个恒定的间隔,直到第一个指针到达最后一个结点。此时第二个指针将指向从最后一个结点数起的第 n 个结点。我们重新链接第二个指针所引用的结点的 next 指针指向该结点的下下个结点。

代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dump = new ListNode(0);
dump.next = head;
ListNode first = dump;
ListNode second = dump;
for (int i=1; i<=n+1; i++) {
first = first.next;
}
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dump.next;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法3 递归法
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
return removeNode(head,n)==n?head.next:head;
}
public int removeNode(ListNode node,int n) {
if(node.next == null) return 1;
int m = removeNode(node.next, n);
if(m == n)
if(m == 1) node.next = null;
else node.next = node.next.next;
return m+1;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
24 两两交换链表中的节点
题目描述
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3.
解法1 递归法
从链表的头节点
head开始递归。每次递归都负责交换一对节点。在所有节点交换完成以后,我们返回交换后的头,即原始链表的第二个节点。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head.next;
first.next = swapPairs(second.next);
second.next = first;
return second;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
解法2 迭代法
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dump = new ListNode(0);
dump.next = head;
ListNode prev = dump;
while (head != null && head.next != null) {
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head.next;
prev.next = second;
first.next = second.next;
second.next = first;
prev = first;
head = first.next;
}
return dump.next;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
445 两数相加II(链表求和)
题目描述
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) 输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
解法1 链表反转,按位相加
将链表反转,然后按位相加,并通过carry记录进位的值。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode node1 = reverse(l1);
ListNode node2 = reverse(l2);
// 记录进位值
int carry = 0;
ListNode head = null;
while (node1 != null || node2 != null || carry != 0) {
int sum = 0;
int n1 = node1 == null ? 0 : node1.val;
int n2 = node2 == null ? 0 : node2.val;
node1 = node1 == null ? node1 : node1.next;
node2 = node2 == null ? node2 : node2.next;
// 链表按位相加
sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum%10);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return head;
}
// 链表反转
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(max(m,n))$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
解法2 辅助栈
本题的主要问题在于链表中数位的顺序与我们做加法的顺序是相反的,为了逆序处理所有数位,我们可以使用栈:把所有数字压入栈中,再依次取出相加。然后反转链表返回。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = stackPush(l1);
Stack<Integer> stack2 = stackPush(l2);
int carry = 0;
ListNode head = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0 ) {
int sum = 0;
sum += stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
sum += stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
sum = sum + carry;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum % 10);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return head;
}
private Stack<Integer> stackPush(ListNode node) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while(node != null) {
stack.push(node.val);
node = node.next;
}
return stack;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(max(m,n))$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(m+n)$ |
234 回文链表
题目描述
判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
输入: 1->2->3->2->1 输出: true
解法1 链表反转(🌟)
将链表反转,然后与原链表进行比较。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = reverse(head);
while (head != null && node != null) {
if (head.val != node.val) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
node = node.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
ListNode cur = new ListNode(head.val);
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
####解法2 双指针法
将链表中的值添加到数组中,然后设置头尾指针一起向内移动判断是否是回文。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 初始化一样空数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
// 把链表中的值存到数组中
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
// 头指针
int front = 0;
// 尾指针
int back = list.size() - 1;
while (front < back) {
// 比较头尾指针的值是否相同,相同的话头尾指针均向内移动,继续遍历比较,不同则返回
if (!list.get(front).equals(list.get(back))) {
return false;
}
front ++;
back --;
}
return true;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
####解法3 递归法
使用递归遍历链表,然后头尾节点值进行比较。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode frontPointer;
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
frontPointer = head;
return reverse(head);
}
private boolean reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head != null) {
if (!reverse(head.next)) return false;
if (frontPointer.val != head.val) return false;
frontPointer = frontPointer.next;
}
return true;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
####解法4 双指针+链表反转
将链表的后半部分反转(修改链表结构),然后将前半部分和后半部分进行比较。比较完成后将链表恢复原样。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return true;
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverse(firstHalfEnd.next);
ListNode node1 = head;
ListNode node2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
while ( result && node2 != null) {
if (node1.val != node2.val) return false;
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
firstHalfEnd.next = reverse(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
725 分隔链表
题目描述
给定一个头结点为 root 的链表, 编写一个函数以将链表分隔为 k 个连续的部分。每部分的长度应该尽可能的相等: 任意两部分的长度差距不能超过 1,也就是说可能有些部分为 null。这k个部分应该按照在链表中出现的顺序进行输出,并且排在前面的部分的长度应该大于或等于后面的长度。返回一个符合上述规则的链表的列表。
输入: root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], k = 3 输出: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10]] 解释: 输入被分成了几个连续的部分,并且每部分的长度相差不超过1.前面部分的长度大于等于后面部分的长度。
解法1 创建新链表
首先计算链表的总节点数n,然后通过n/k得到分割的链表节点数,如果n%k不为0,则需要在分隔的节点上都依次加1,然后创建一个新链表,把分隔的列表写入新链表。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode cur = root;
while (root != null) {
root = root.next;
n++;
}
// 分段
int length = n/k;
// 余数
int rem = n%k;
ListNode[] list = new ListNode[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0), write = head;
for (int j = 0; j < length + (i < rem ? 1 : 0); j++) {
write = write.next = new ListNode(cur.val);
if(cur != null) cur = cur.next;
}
list[i] = head.next;
}
return list;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n+k)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(max(n,k))$ |
解法2 拆分链表
同解法1类似,此处只是拆分原链表。
代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
n++;
}
// 分段
int length = n/k;
// 余数
int rem = n%k;
ListNode[] list = new ListNode[k];
cur = root;
for (int i = 0; cur != null && i < k; i++) {
list[i] = cur;
for (int j = 0; j < length + (i < rem ? 1 : 0) - 1; j++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = next;
}
return list;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n+k)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(k)$ |
328 奇偶链表
题目描述
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
解法1 双指针法
将奇节点放在一个链表里,偶链表放在另一个链表里。然后把偶链表接在奇链表的尾部。用变量
head和odd保存奇链表的头和尾指针。evenHead和even保存偶链表的头和尾指针。

代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode odd = head, even = head.next, evenHead = even;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | $O(n)$ |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $O(1)$ |
2 两数相加
题目描述
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) 输出:7 -> 0 -> 8 原因:342 + 465 = 807
解法1 初等数学
新创建一个链表head,遍历两个非空链表,设置一个进位值carry,初始值为0,把链表值与进位值相加取余,即为新链表的值,同时更新进位值,当遍历完成之后,如果进位值为1,则返回列表追加一个含有数字 1 的新结点。
代码实现
package com.cn.algorithm.array;
import com.cn.algorithm.linklist.ListNodeOutPut;
import com.cn.algorithm.util.ListNode;
/**
* @Author: cyh
* @Date: 2020-04-26 18:19
* @Description: 两数相加
**/
public class AddTwoNumbers {
/**
* 两数相加-初等数学
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, cur = head;
int sum = 0, carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = (p != null) ? p.val : 0;
int y = (q != null) ? q.val : 0;
sum = x + y + carry;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur.next;
carry = sum / 10;
if (p != null) p = p.next;
if (q != null) q = q.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddTwoNumbers demo = new AddTwoNumbers();
System.out.println("-------------------初始链表----------------");
ListNode node = ListNodeOutPut.listNodeOut();
System.out.println("-------------------两数相加----------------");
ListNode node1 = demo.addTwoNumbers(node, node);
ListNodeOutPut.resultOut(node1);
}
}
复杂度分析
| 时间复杂度 | O(max(m,n)) |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | O(max(m,n)) |